
Safety Torque Off as the basis for all other safety functions
- No Comments
The most common and basic safety function drive is the Safety Torque Off (STO). This is also called “uncontrolled shutdown” and is a function that results in an immediate interruption of the power supply to the drive elements. It corresponds to stop category 0 according to EN 60204-1 and after shutdown, it is unable to generate any torque. The drive can also no longer generate a braking torque and the braking must be carried out by separate measures such as a mechanical brake, so that no undesired overrun or overshooting of end bearings occurs. The STO safety function forms the basis of all other safety functions, such as SS1, SS2 or SOS. It is the implementation of the closed-circuit current principle and is always assumed in the event of a fault.
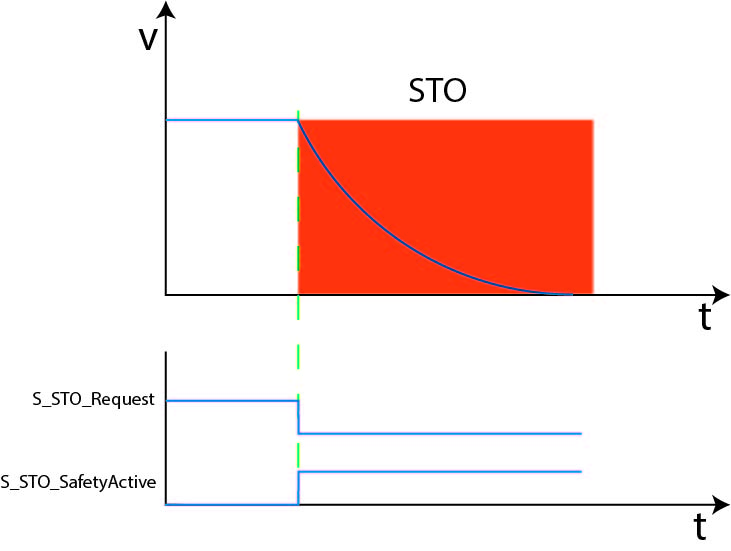
Immediately after STO activation, the drive is set torque-free and the axis runs down until zero speed is reached.
The safety function (STO) is executed immediately upon request. STO can be requested by controlling the signal at input S_STO_Request to SAFEFALSE or via the hardwired connection. The torque-free state of the drive is indicated by controlling the block output S_STO_SafetyActive to SAFETRUE. After displaying the active STO function, the axis coast down. The coasting time depends on physical properties, such as weight, torque or even friction.
The design of a machine is often a tightrope walk between lowest possible costs and high safety. It is important to keep the potential hazards as low as possible. The machine directives and the associated safety standards provide defined and binding rules for hazard analysis and reduction. Typical applications are the STO of inverters, shutdown via contactors or main switches with emergency stop function, torque separation with a clutch.
The design of a machine is often a tightrope walk between lowest possible costs and high safety. It is important to keep the potential hazards as low as possible. The machine directives and the associated safety standards provide defined and binding rules for hazard analysis and reduction. Typical applications are the STO of inverters, shutdown via contactors or main switches with emergency stop function, torque separation with a clutch.


